“Schubert at the Piano II“ (1899)
______
for the second evening of Schubert sonatas
during my May Schubertiade, it wouldn’t be
surprising to hear again an early work, 1819,
Schubert would’ve been 22, the series is
undoubtedly and necessarily somewhat
chronological
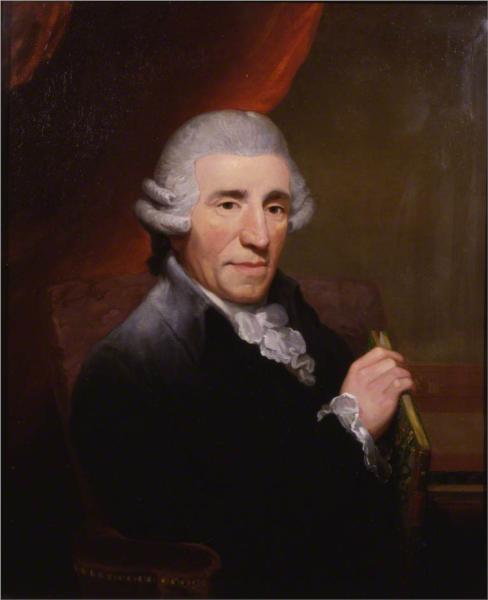
blatantly anchored in the Classical idiom,
you can hear Mozart all over the place, not
all pejoratively, Mozart is effervescent, full
of exuberance and creativity, Schubert
diligently follows
but Romanticism equals intimacy, poignancy,
which Schubert touches upon in his andante,
the second movement, to a degree not yet
as markedly as, for instance, Chopin yet,
famous for his sweeping Romanticism, but
still convincing and promising
the third movement, the allegro, is right back
at Mozart, to delight the aristocracy, his
essential audience, see above
R ! chard








.jpg!Large.jpg)
